Blocks
Overview
Blocks are individual pieces of your site’s web page layout. They are placed inside the regions of your theme, and can be created, removed, and rearranged in the Block layout (admin/structure/block) administration page. Examples of blocks include the Who’s online listing, the main navigation menu, and the breadcrumb trail. The main page content is also a block.
Some modules make new blocks available for placement on your site. For example, when the core Search module is installed and configured, it provides a block that contains a search form. You may also create and place your own custom blocks.
Each block has its own configuration settings, which allow you to select which pages of your site will display the block. It is even possible to place multiple copies of a block, each with its own separate configuration and visibility rules.
Different types of blocks
- Content Blocks: These are custom blocks created by site administrators or content editors. They are typically used to display static or dynamic content that is specific to the site. Examples include promotional banners, custom messages, or embedded media.
- Custom Blocks: These are blocks provided by Drupal core, contributed or custom modules. They often contain dynamic content or functionality, such as the main navigation menu, user login form or recent content lists (using views). These blocks are automatically available when the corresponding module is enabled. They allow site builders to add custom content or functionality without writing code. Custom blocks can be configured to appear on specific pages or under certain conditions.
Block Management
You can view content blocks at Admin -> Content -> Blocks.
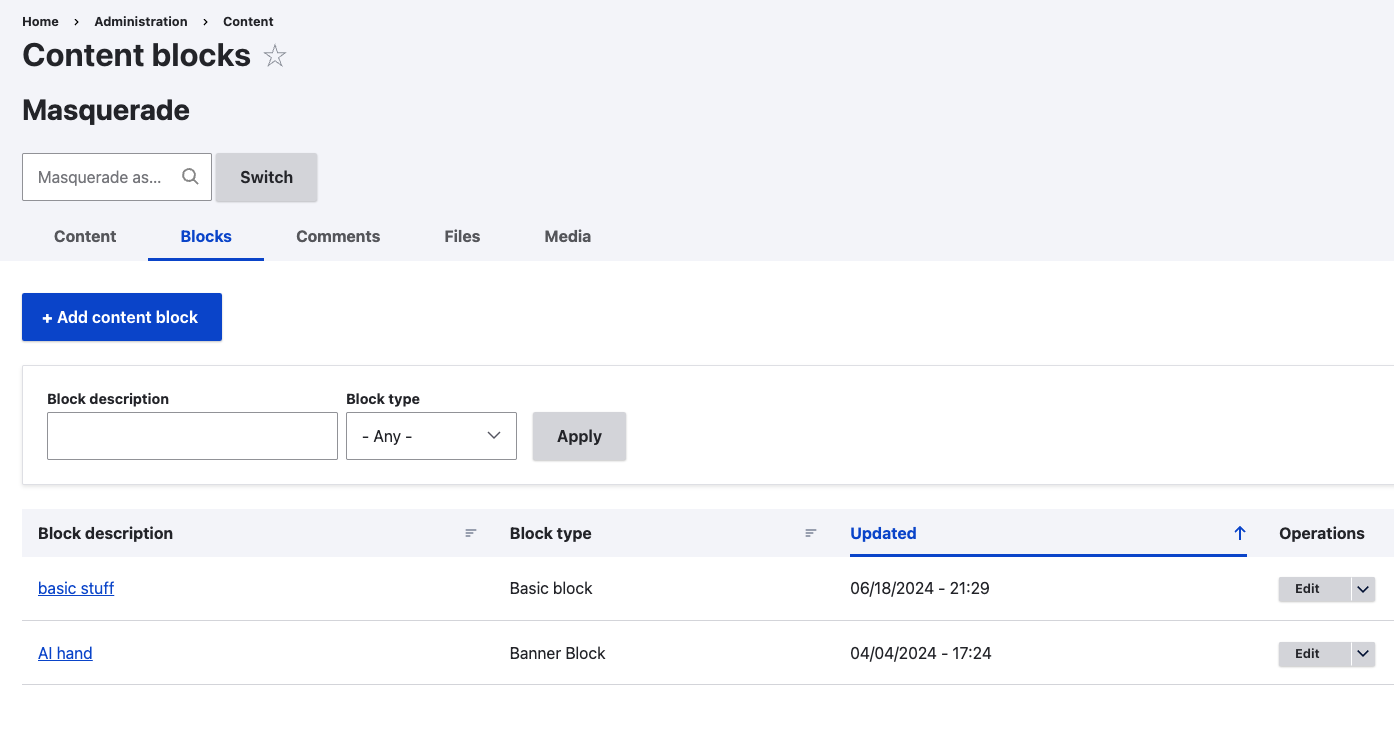
Blocks can be found at Admin -> Structure -> Block layout.
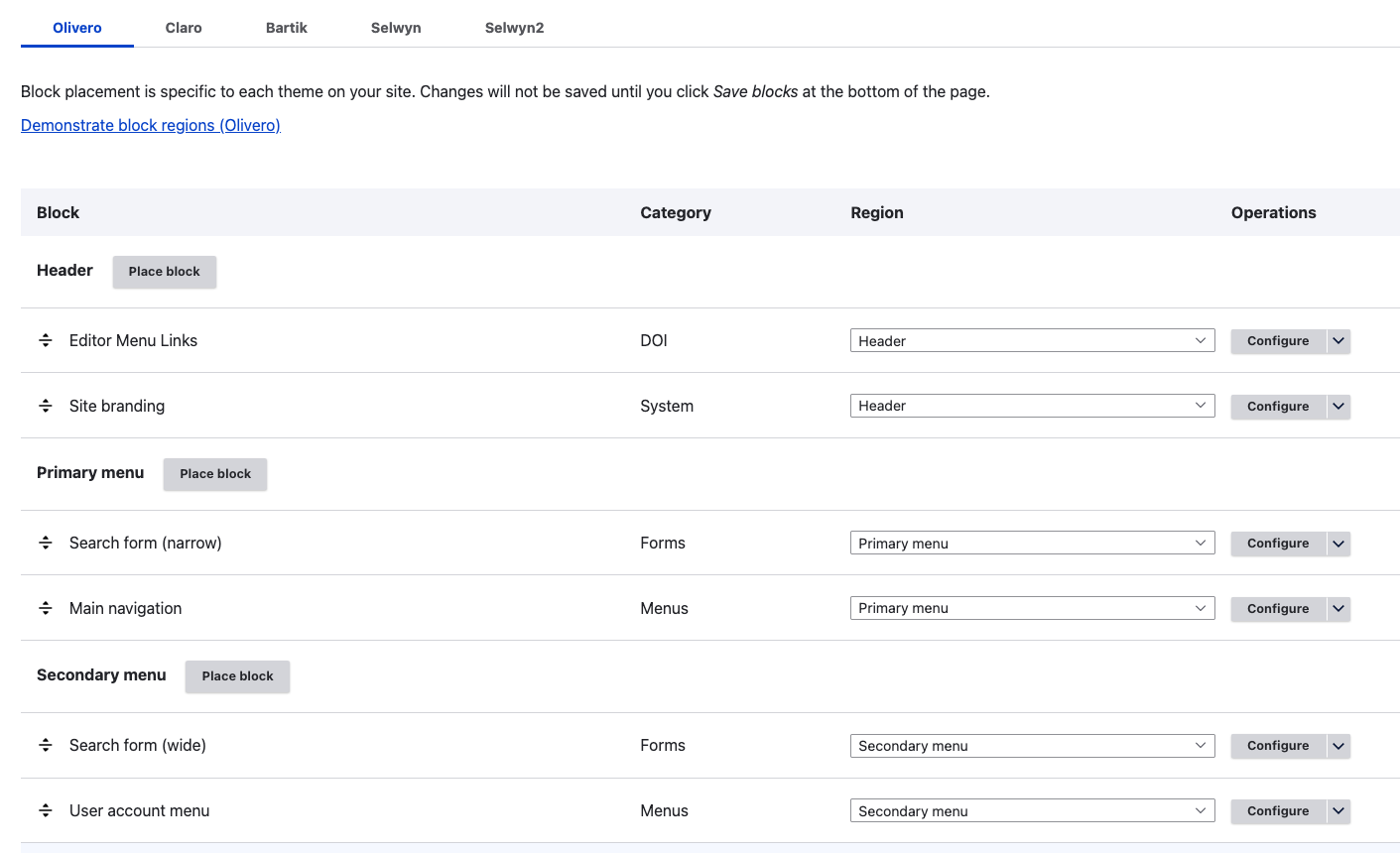
You can configure a specific block by clicking the Configure button next to that block. This is the search block (narrow):
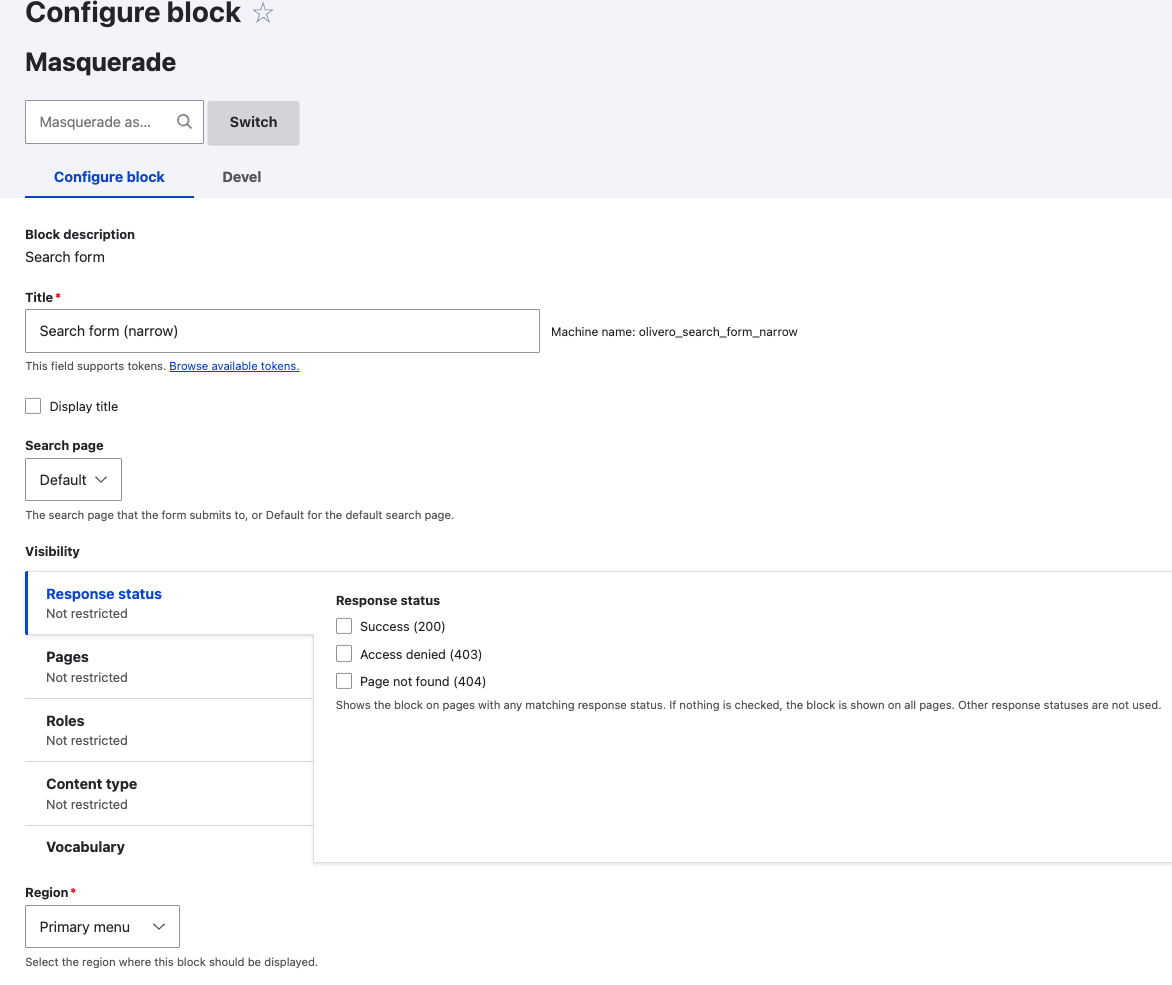
Block Visibility
You can configure a blocks visibility settings (i.e. where they will and won't show up), based on:
Language (If Multilingual is enabled)
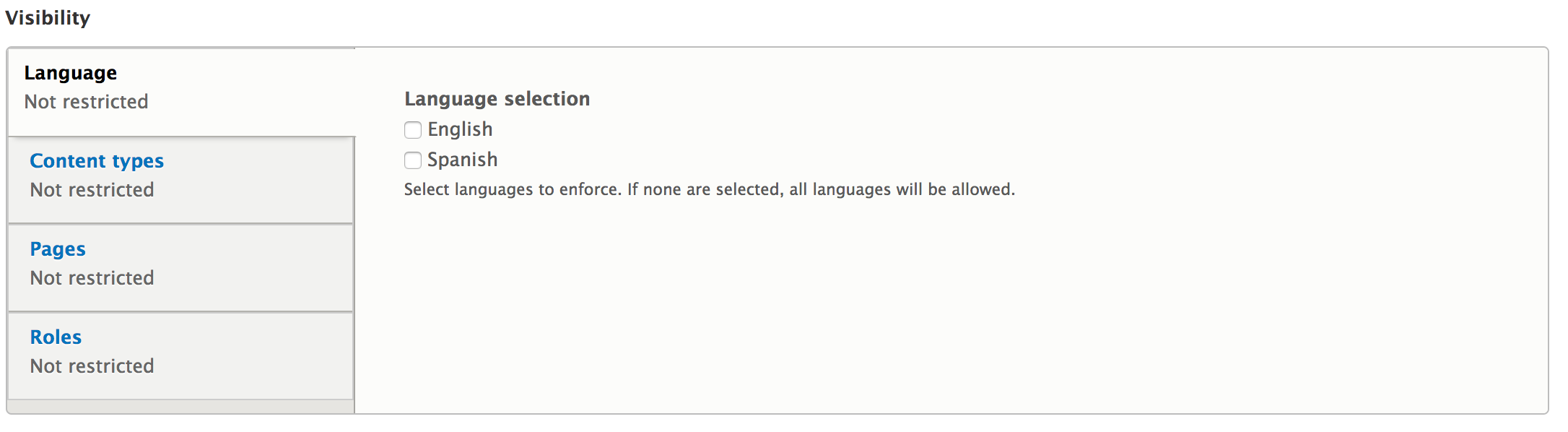
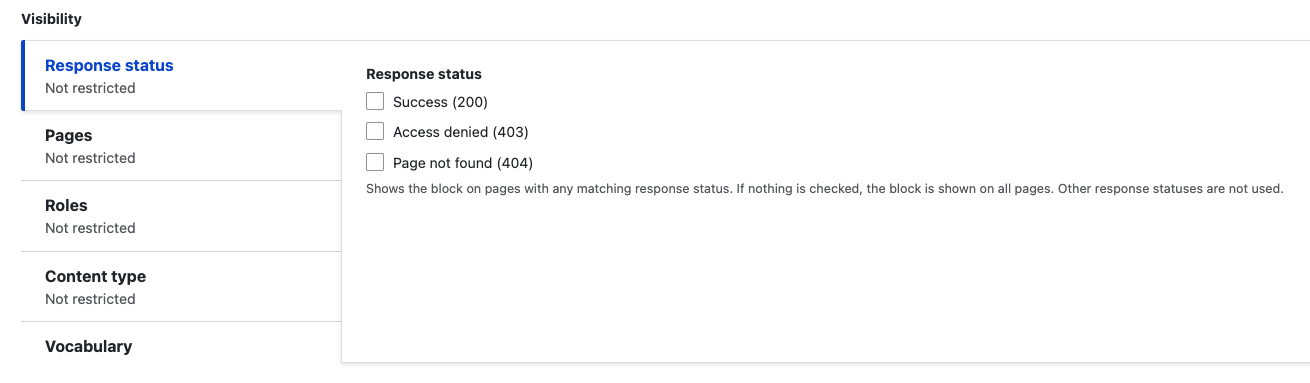
Response type: Shows the block on pages with any matching response status. If nothing is checked, the block is shown on all pages. Other response statuses are not used.
Pages: Specify pages by using their paths. Enter one path per line. The
*character is a wildcard. An example path is/user/*for every user page.<front>is the front page.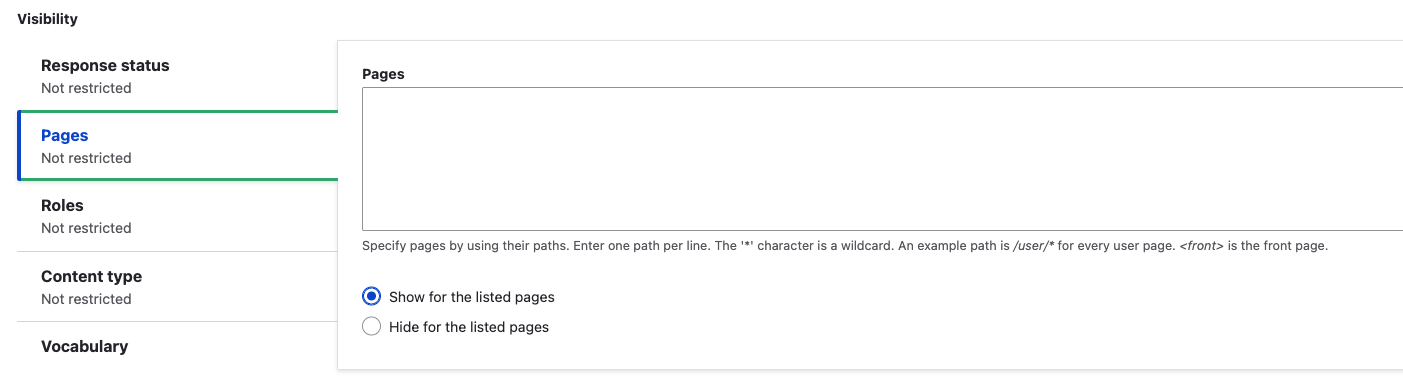
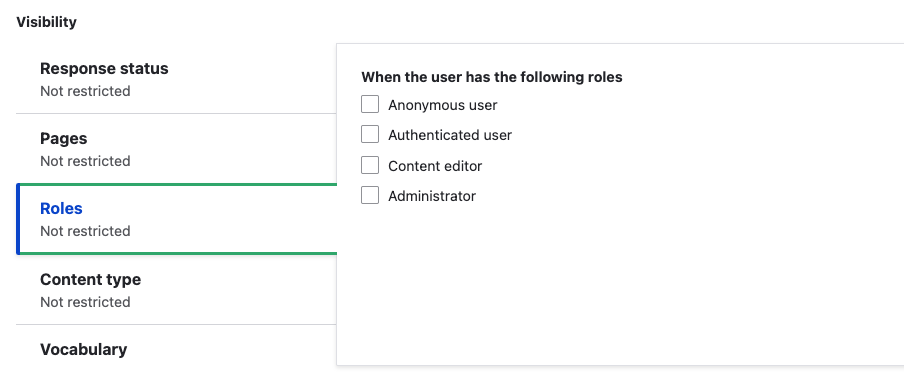
Roles: Specify the roles that will see the block. If no roles are checked, the block is shown to all users.
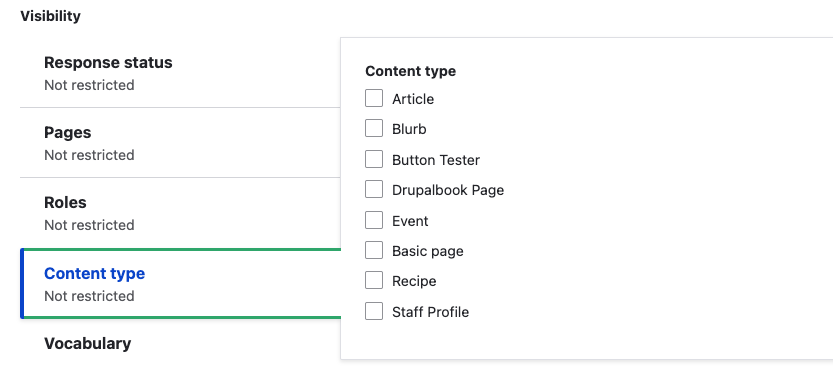
Content Type: Specify the content types that will see the block. If no content types are checked, the block is shown to all content types.
Vocabulary: Specify the vocabularies that will see the block. If no vocabularies are checked, the block is shown to all vocabularies.
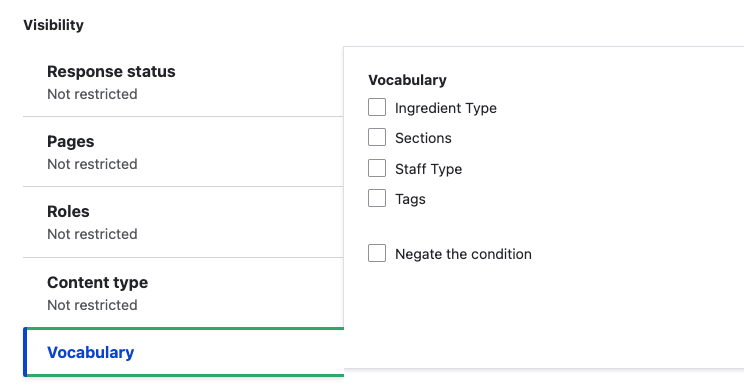
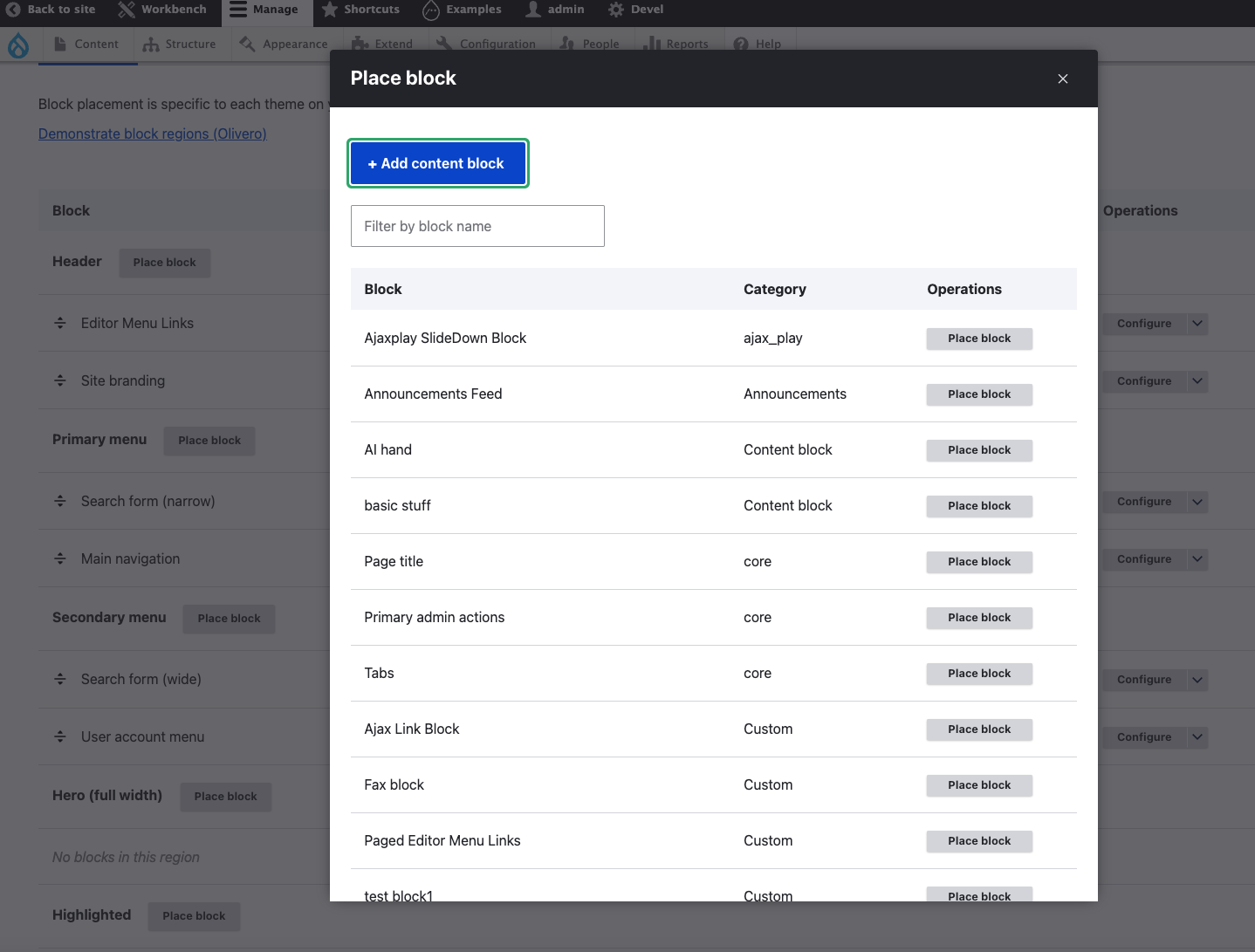
Block Placement
You can either place a specific block into a region by configuring the block, or by clicking the "Place block" button for a particular region on the Block layout page.
Resources
Questions
What are blocks in Drupal, and how are they used in site layout?
Blocks are individual pieces of content used to build a site's layout. They are placed in theme regions and can display static or dynamic content, like menus, breadcrumbs, or custom elements. Blocks can be created, configured, and arranged in the Block layout page.
What types of blocks are available in Drupal, and what distinguishes custom blocks from content blocks?
Content blocks are custom blocks created by administrators to display specific content. Custom blocks are provided by Drupal core or modules, often featuring dynamic content or functionality, like login forms or navigation menus.
How can you configure the visibility and placement of blocks in Drupal?
Block visibility can be configured based on criteria like language, user roles, content types, or page paths. Blocks are placed in specific regions via the Block layout page, using the "Place block" button or individual block configuration.
