Multilingual
The Drupal 8 Multilingual Initiative focused on making multilingual support an integral part of core functionality. You now have the option of selecting your default language right during the installation process.
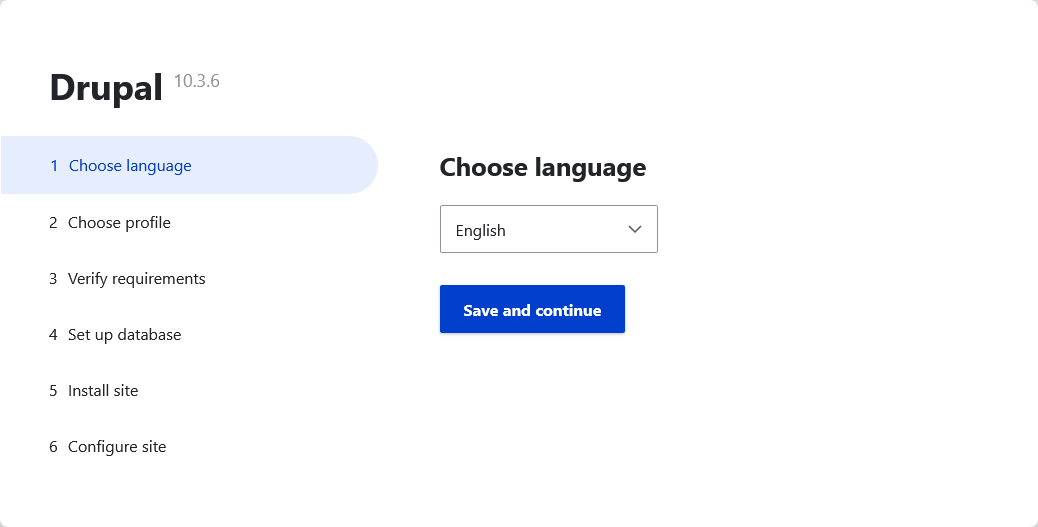
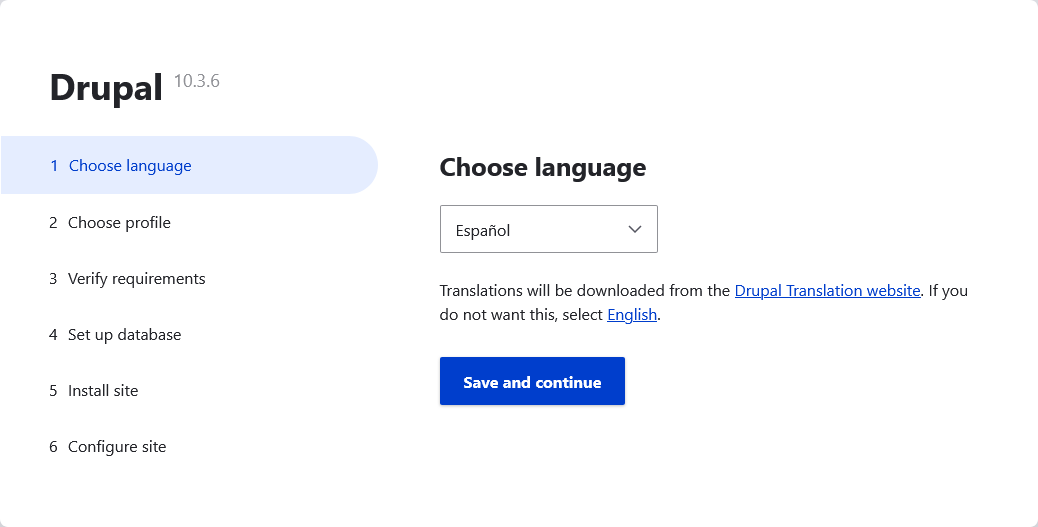
When you select a language other than English, Drupal will automatically enable the necessary multilingual modules (i.e. Language Module and Interface Translation Module), and download the latest translations from localize.drupal.org.
To enable Multilingual functionality on an existing site, go to "Extend" or /admin/modules and find the Multilingual section. "Language" is the base module required for multilingual, but you will likely want at least Content Translation as well.
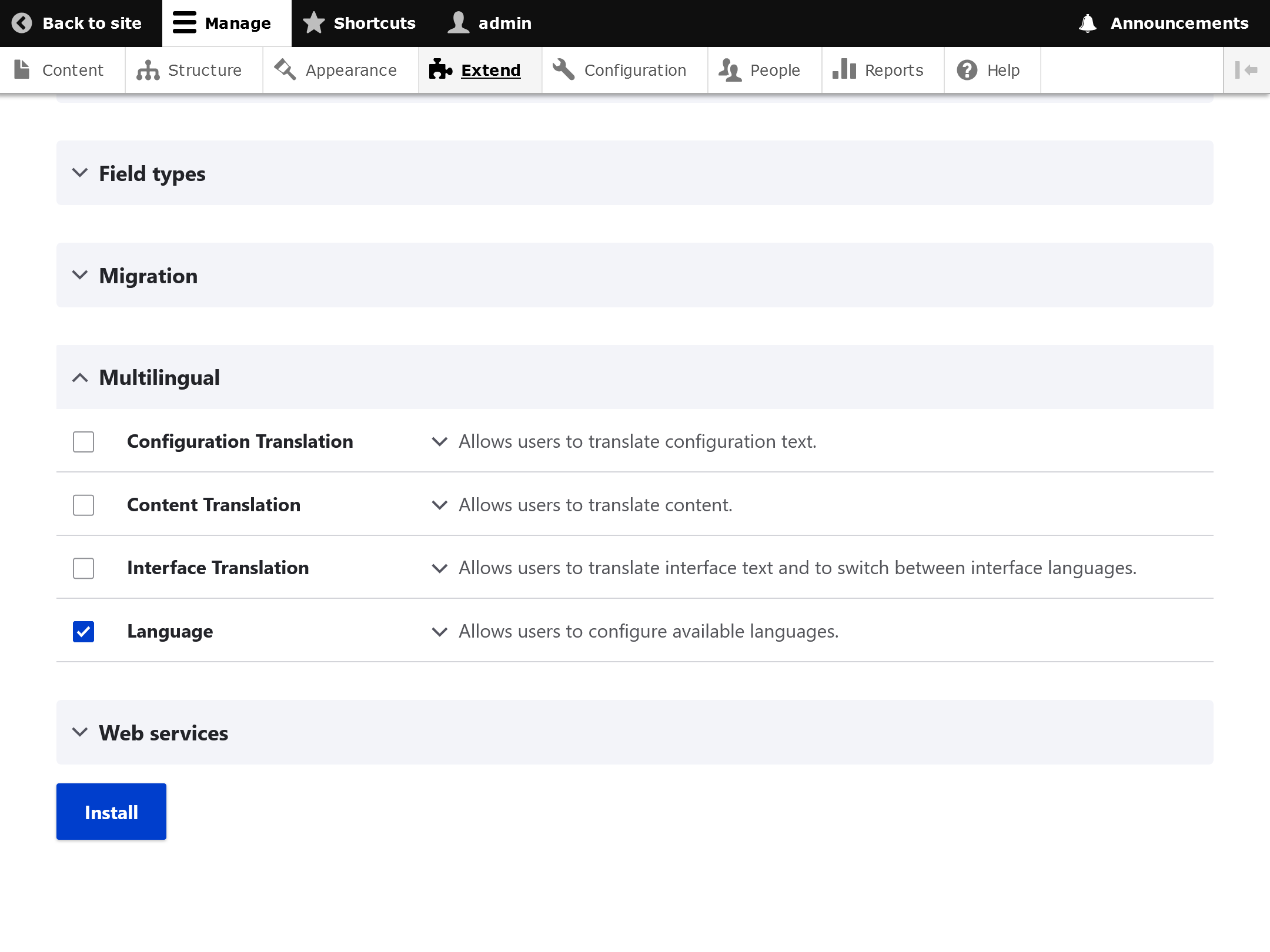
Drupal's multilingual features are enabled by these four modules:
- Language Module
- Interface Translation Module
- Content Translation Module
- Configuration Translation Module
Language Module
(machine name: language)
From Choosing and installing multilingual modules:
The base module needed for any non-English or multi-lingual site. Allows users to configure languages and how page languages are chosen, and apply languages to content.
This module provides a lot of functionality out of the box:
Support for many languages (and always improving)
Language support is always improving. You can keep track and contribute to the localization of Drupal at localize.drupal.org.
To manage language support go to Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Languages
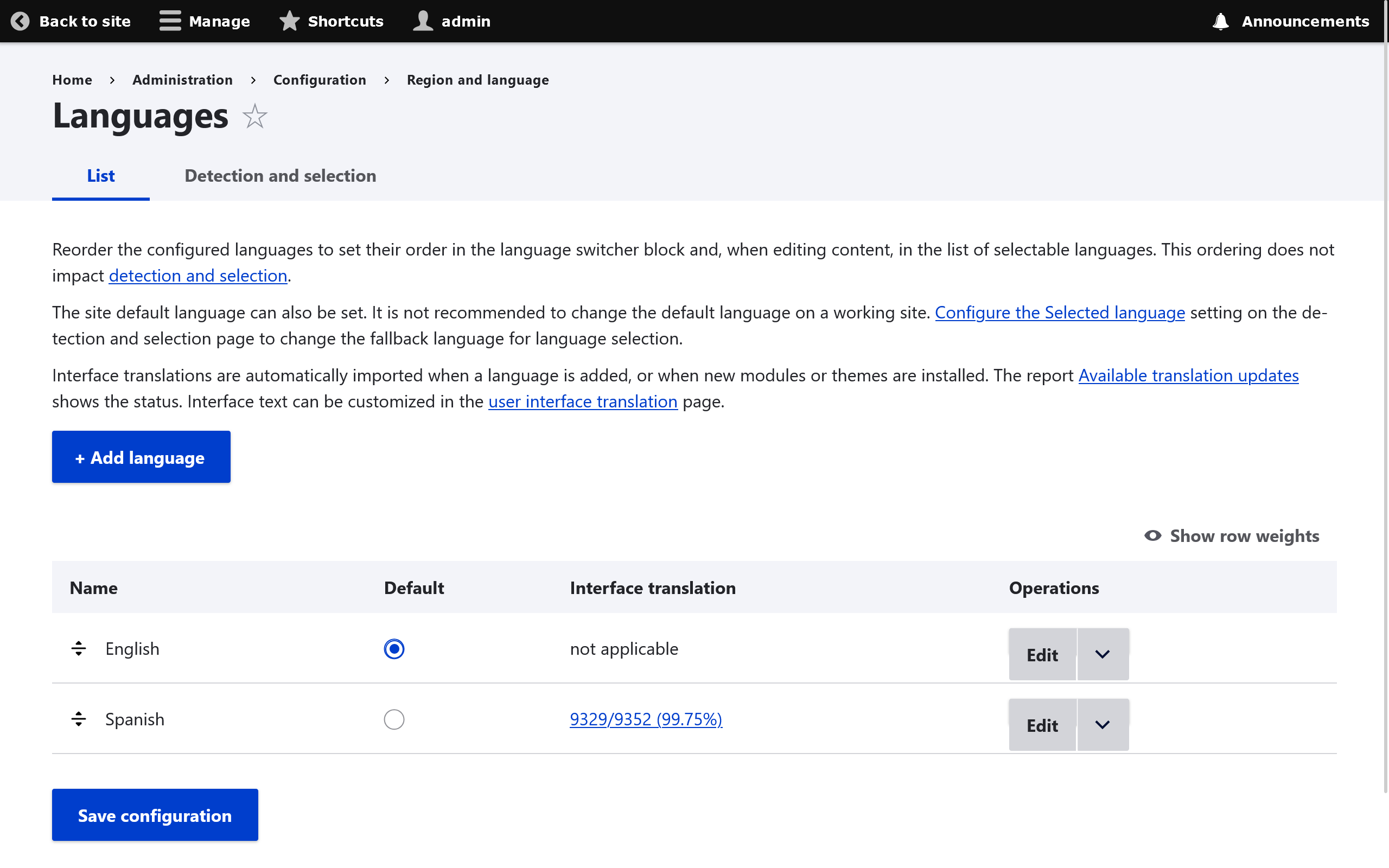
Everything can have a language
Drupal has made all content easily translatable. This includes nodes, users, views, blocks, menus and many other entity-based components.
To specify language options for specific content types:Structure -> Content Types -> (SOME CONTENT TYPE) -> Edit -> Language Settings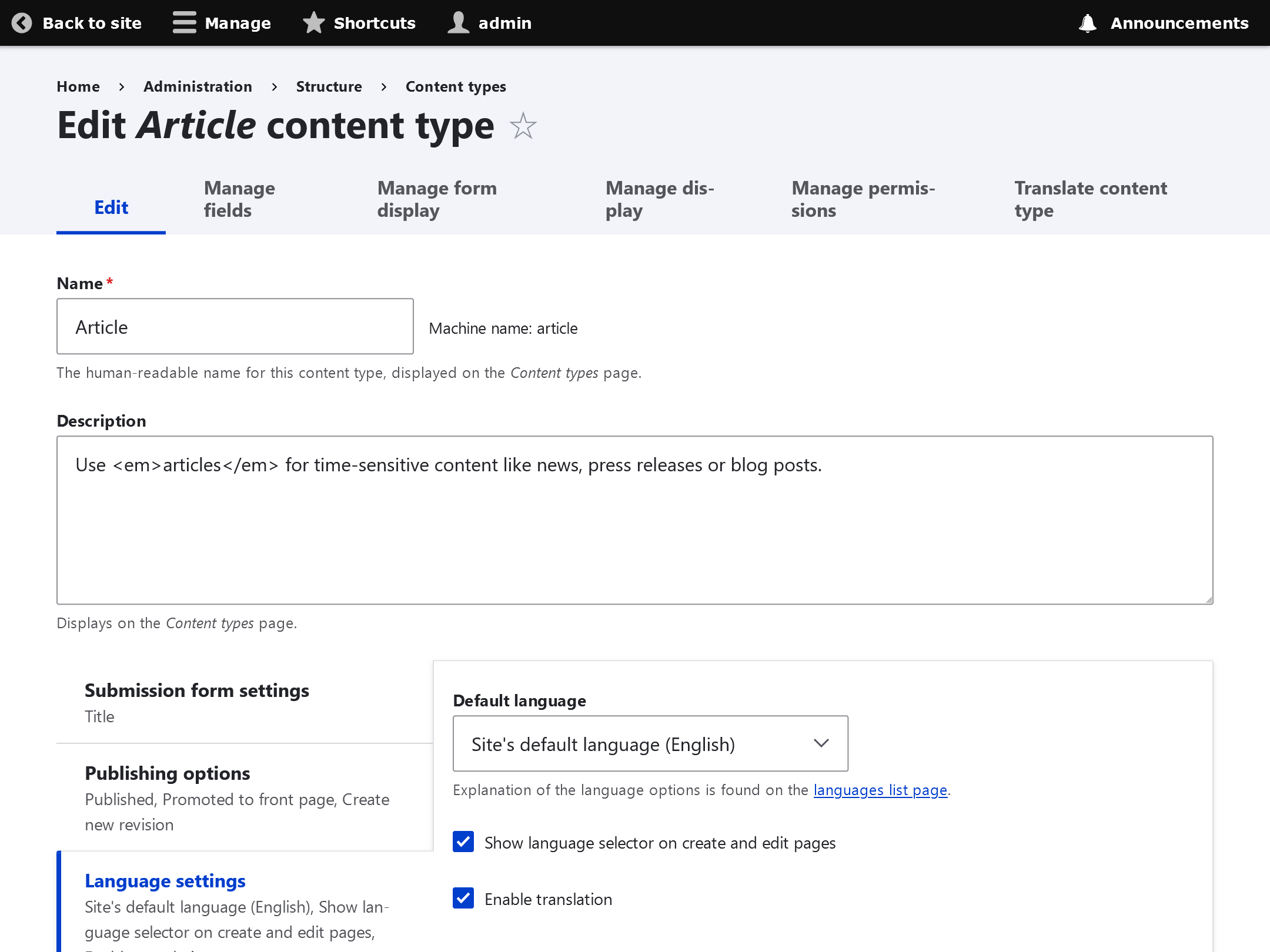
To specify language options for specific blocks:Structure -> Block Layout -> (SOME BLOCK) -> Configure -> Language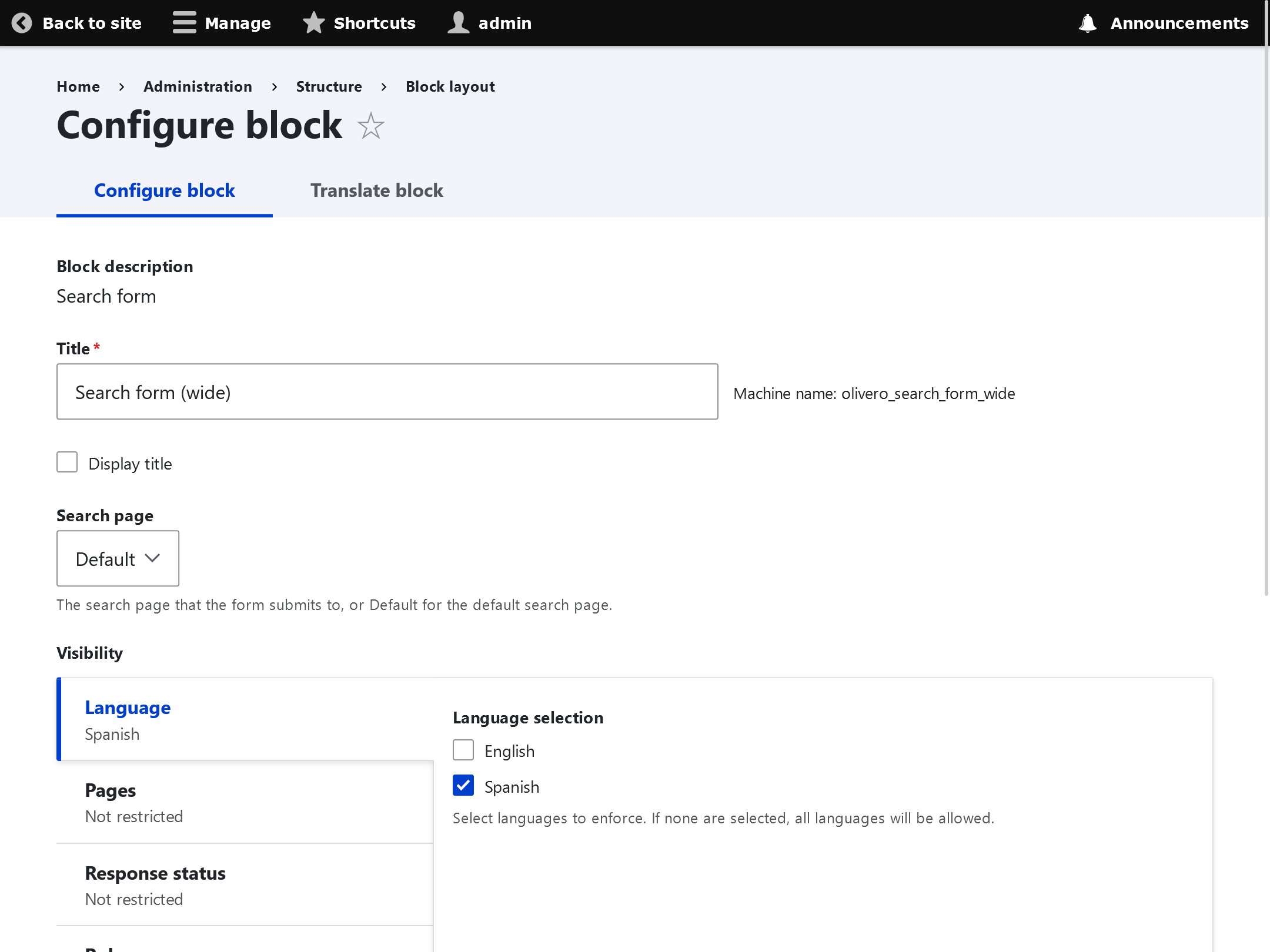
To specify language options for specific menus:Structure -> Menus -> (SOME MENU) -> Edit Menu -> Menu Language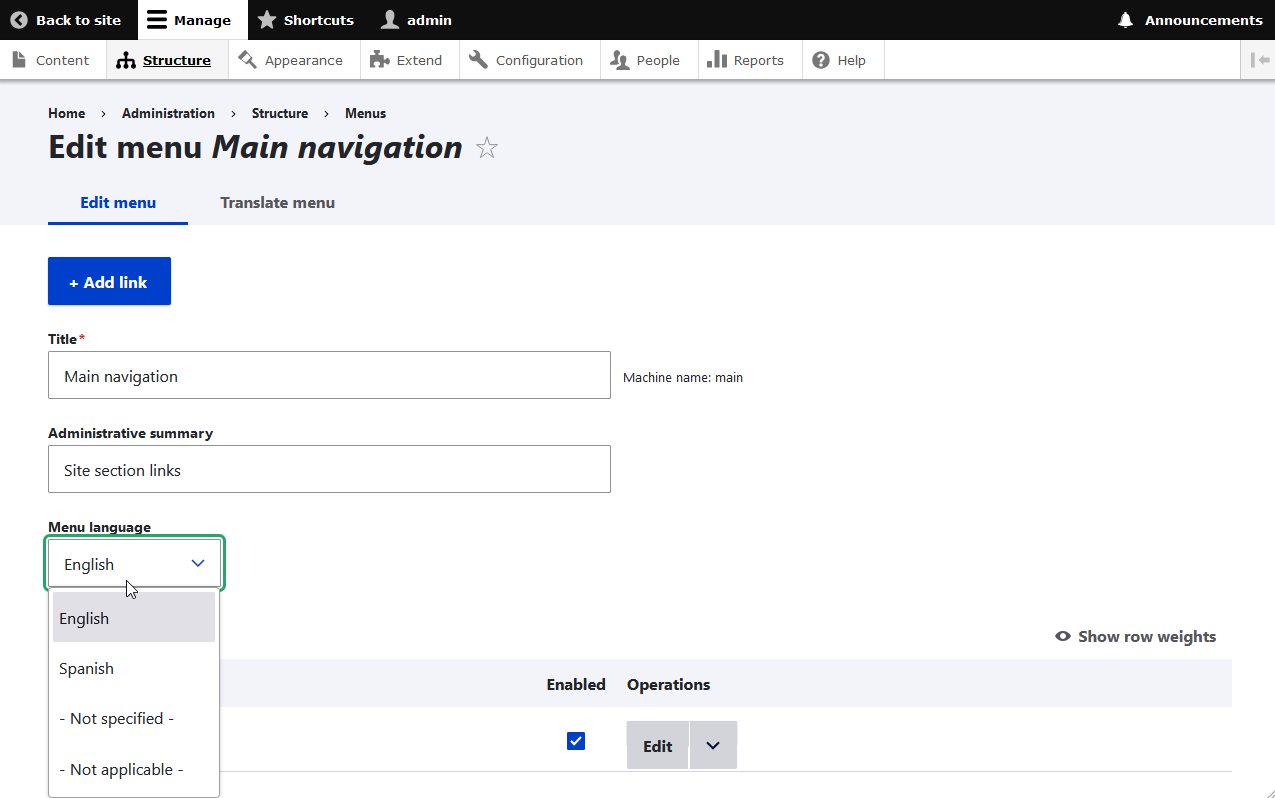
To specify language options for specific users:People -> (SOME USER) -> Edit -> Language Settings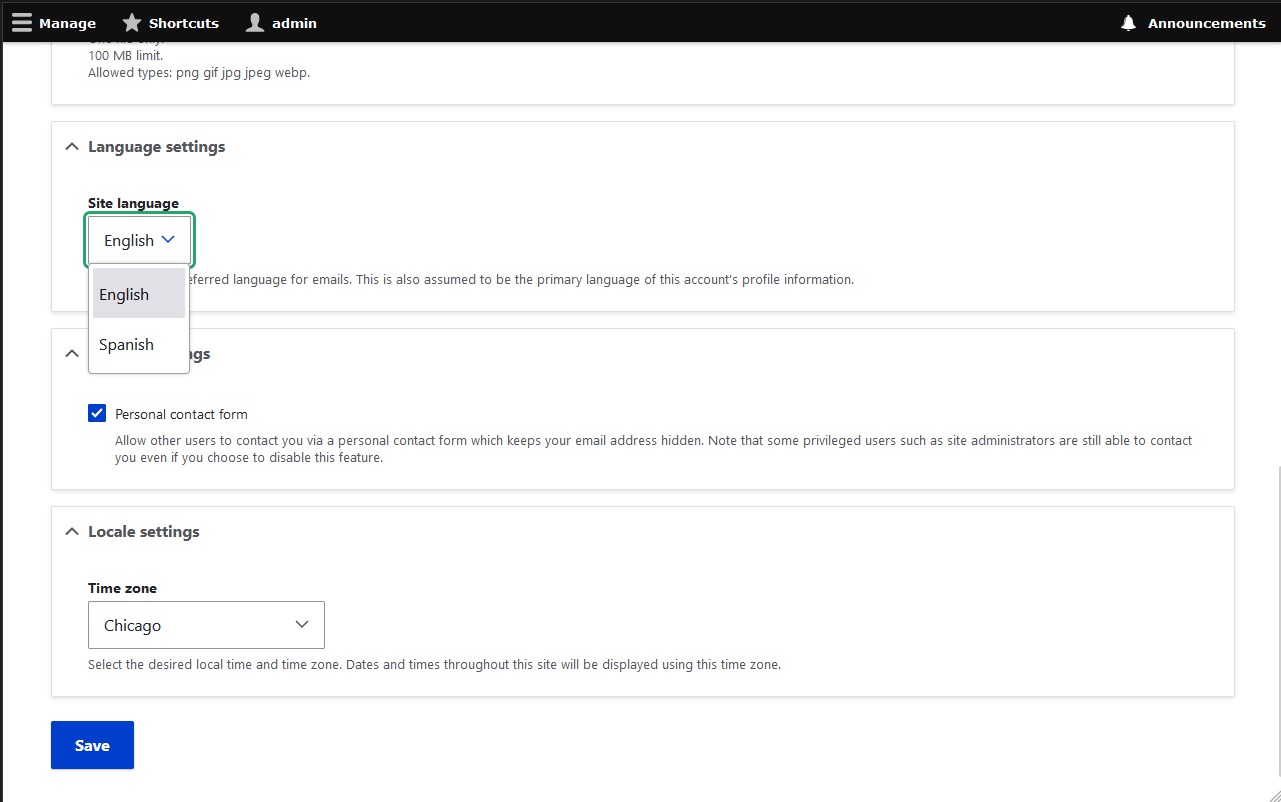
Two special languages
- Language Not Specified (
const LANGUAGE_NOT_SPECIFIED = 'und') - Used when multilingual options are available, but unused for a particular piece of content. This is comparable toLANGUAGE_NONEin Drupal 7. - Language Not Applicable (
const LANGUAGE_NOT_APPLICABLE = 'zxx') - Used when language options do not apply to a particular piece of content (e.g. an image)
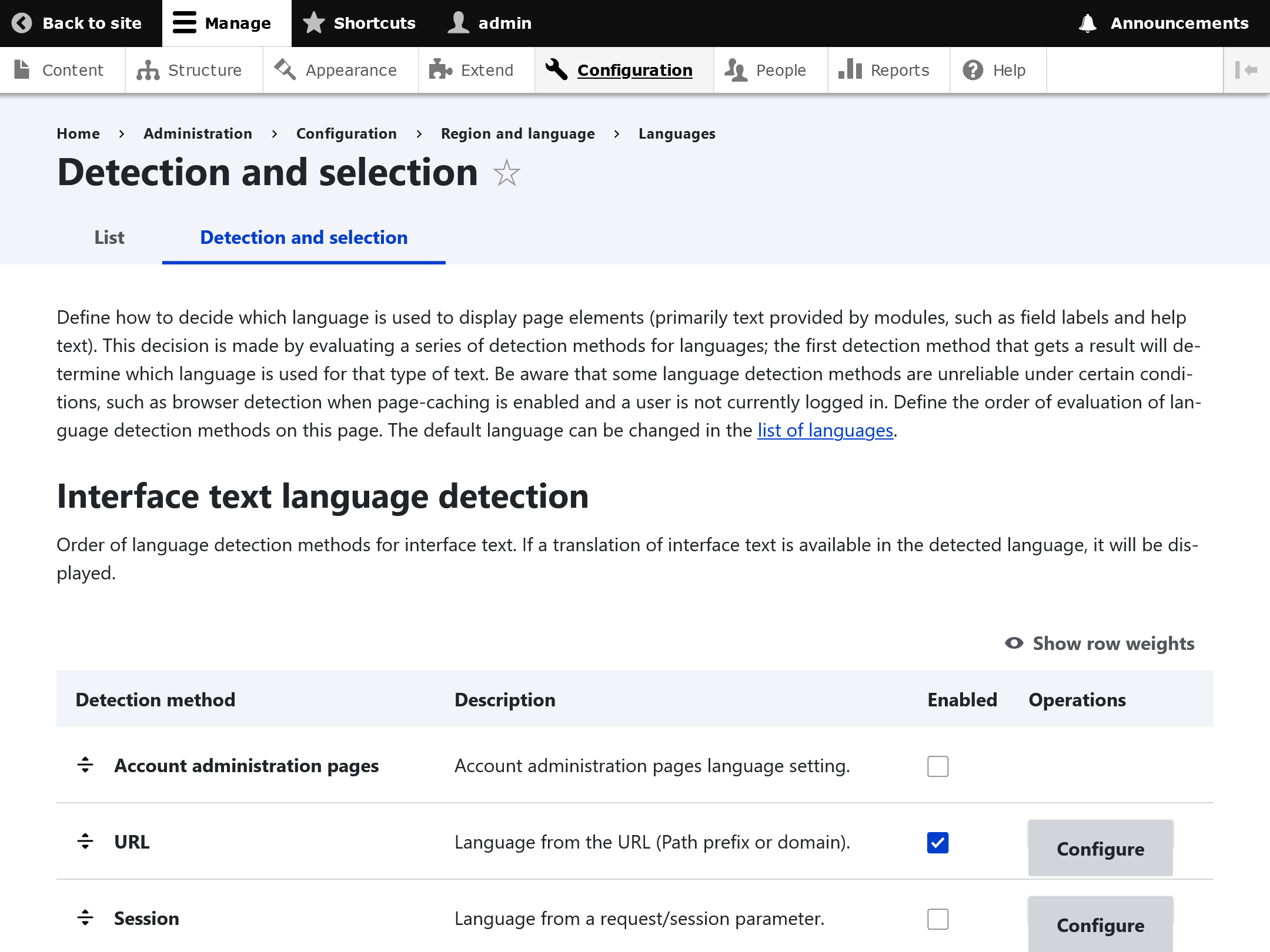
Language negotiation
There are multiple methods to detect which language should be used. You can opt to use as many methods as you want to evaluate a user's language preference.
The options are available, from Enable Language Negotiation:
- URL - Determine the language from the URL (Path prefix or Domain).
- Session - Determine the language from a request/session parameter.
- User - Follow the user's language preference.
- Browser - Determine the language from the browser's language settings.
- Default language - Use the default site language (English).
If multiple methods are selected, Drupal will attempt methods based on their sort order and fallback to the next method if it cannot determine the language based on a particular method.
To change methods and the fallback order go to Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Languages -> Language Detection and Selection
Configurable Browser Language Detection
Browsers use different language codes to refer to the same languages. For example zh-tw, zh-hk and zh-mo may all refer to Chinese Traditional.
Drupal will prepopulate this list based on common browser settings, but this list can be customized at Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Languages -> Language Detection and Selection -> Browser -> Configure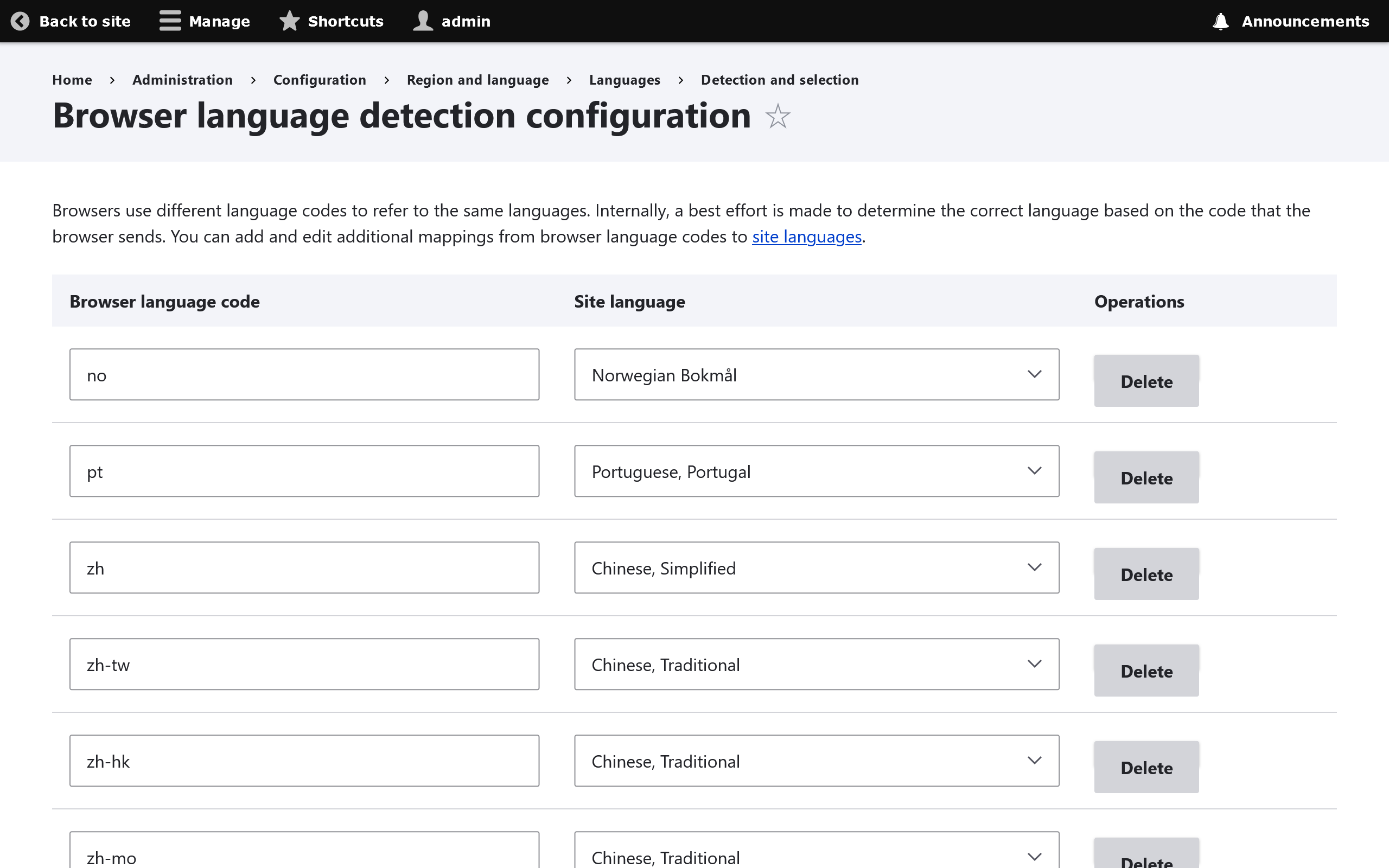
Transliteration
From Transliteration class added:
The core/component transliteration classes do basic character-by-character transliteration using a database of generic character transliterations and language-specific overrides, which is OK for basic uses such as creating legal file names and machine names, but not good for transliterating prose (which would require consideration of context, capitalization, etc.).
Locale (Interface Translation) Module
(machine name: locale)
From Choosing and installing multilingual modules
Translates the built-in user interface, your added modules and themes.
Strings are added to this list by Drupal's StringTranslation service. See Translating site interfaces for details.
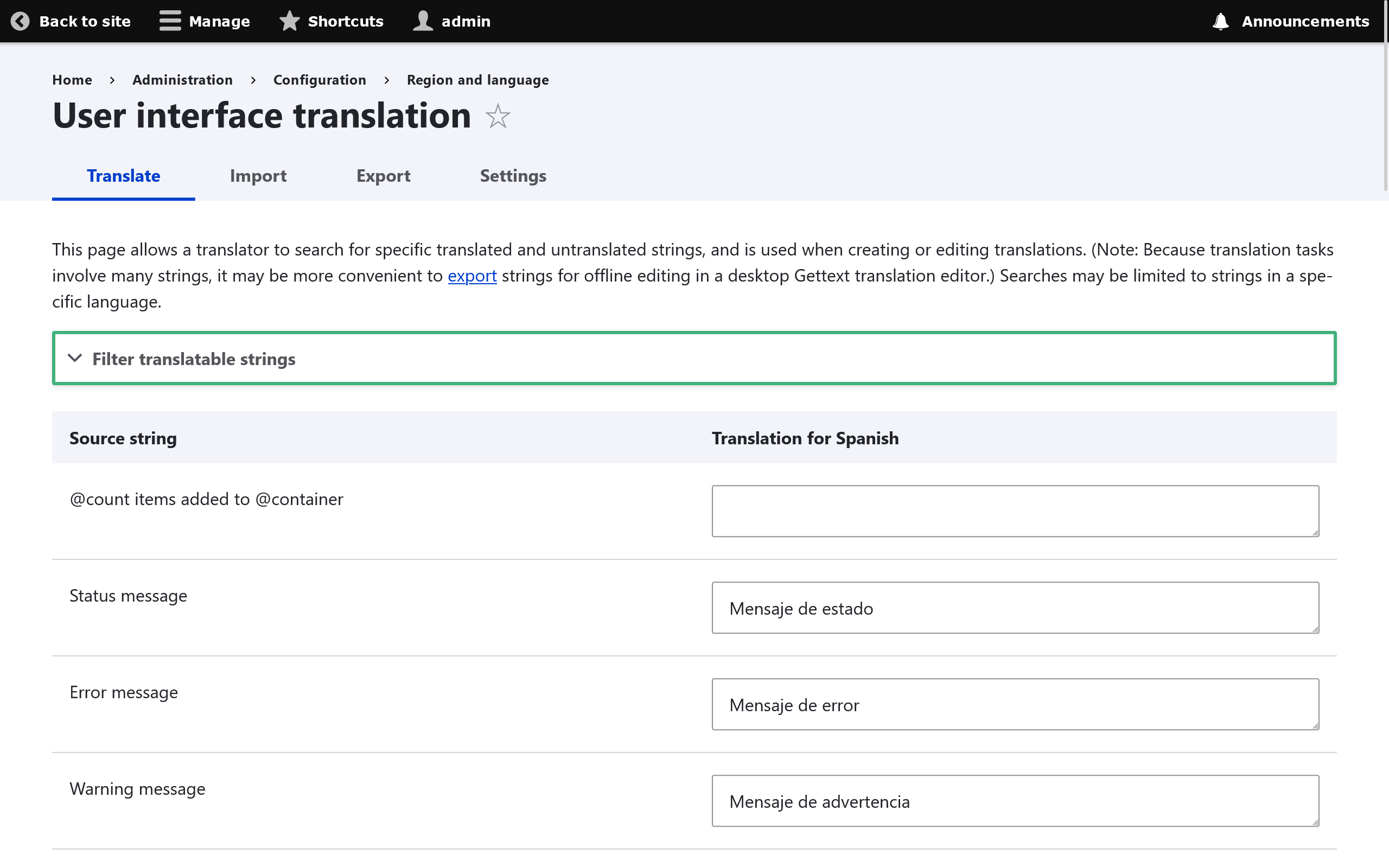
To translate specific UI strings go to: Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Languages -> User Interface Translation and then selecting your language and specifying translation values for each particular string.
To configure your UI translation settings go to: Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Languages -> User Interface Translation -> Settings
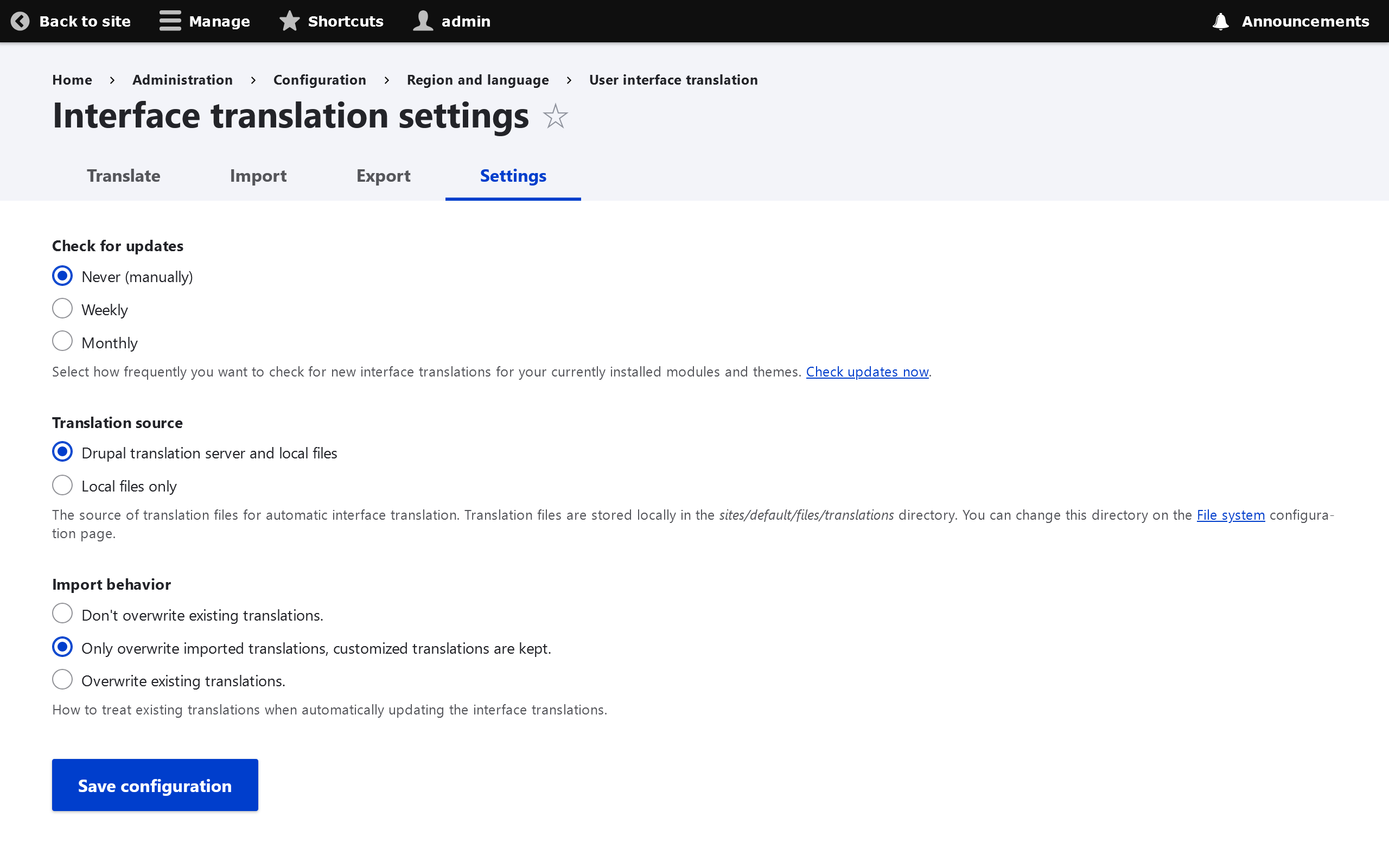
From here you can either configure automatic update language synchronization from localize.drupal.org, or click the Check Updates Now link, to pull down the latest translation strings for your UI.
Content Translation Module
(machine name: content_translation)
From Choosing and installing multilingual modules:
Allows users to translate content entities. Allows you to translate your site content, including pages, taxonomy terms, blocks, etc., into different languages.
Default translation settings
Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Content language and translation. 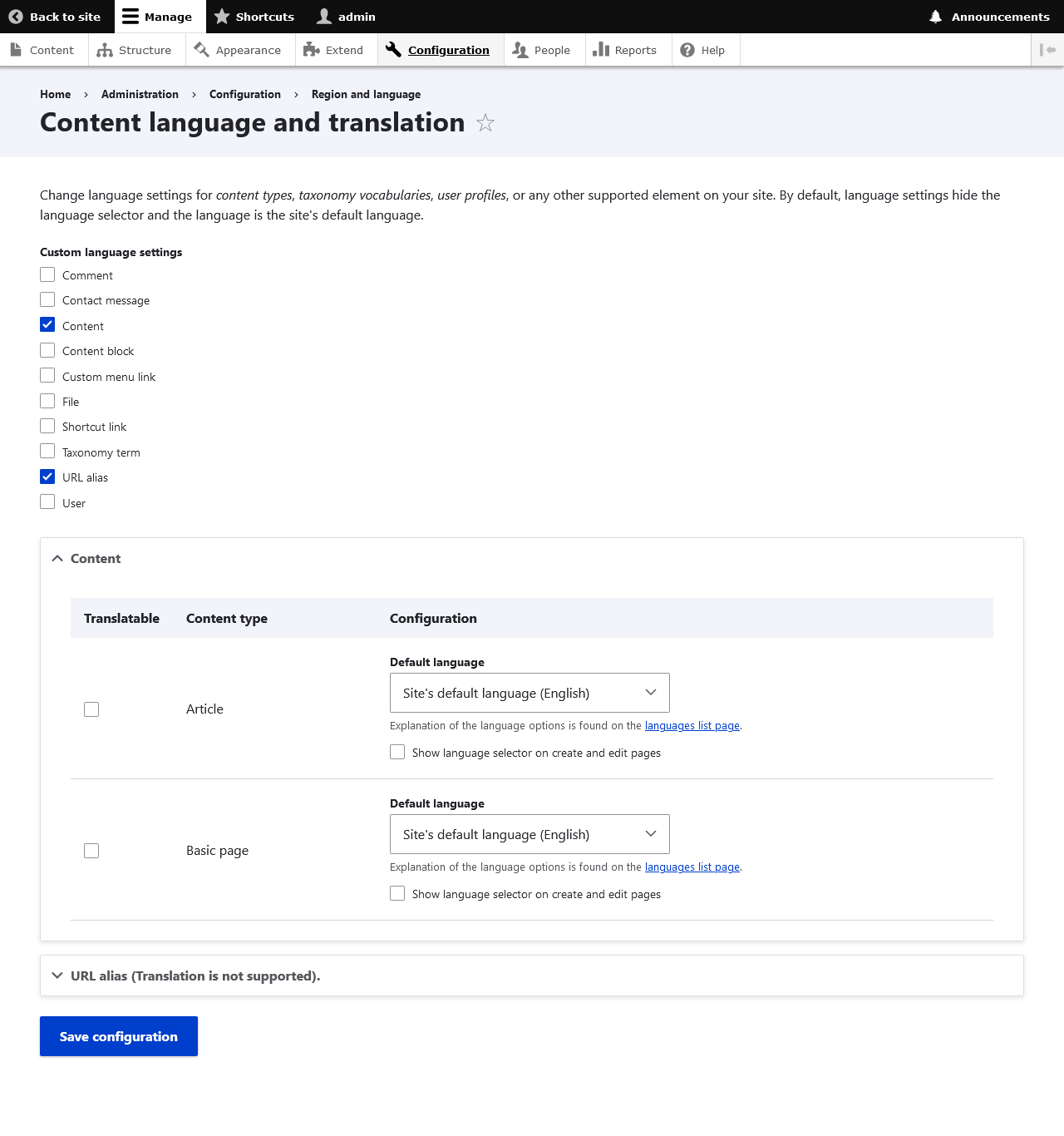
Check the "Translatable" checkbox next to each item you want to translate.
Translating a node
While viewing a node of a content type with translation enabled, you should now see a Translate tab. 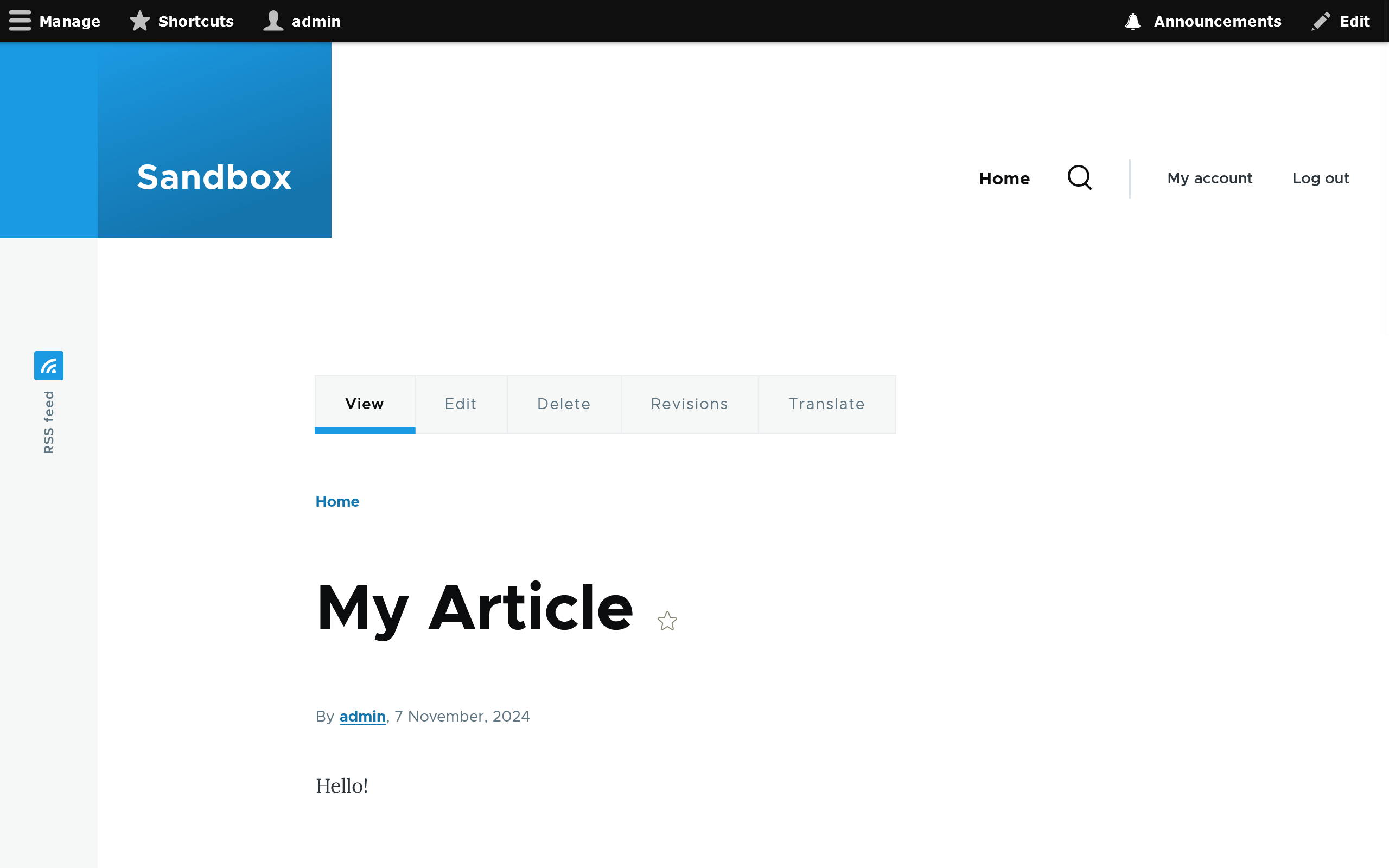
Click Add next to the language you wish to translate. 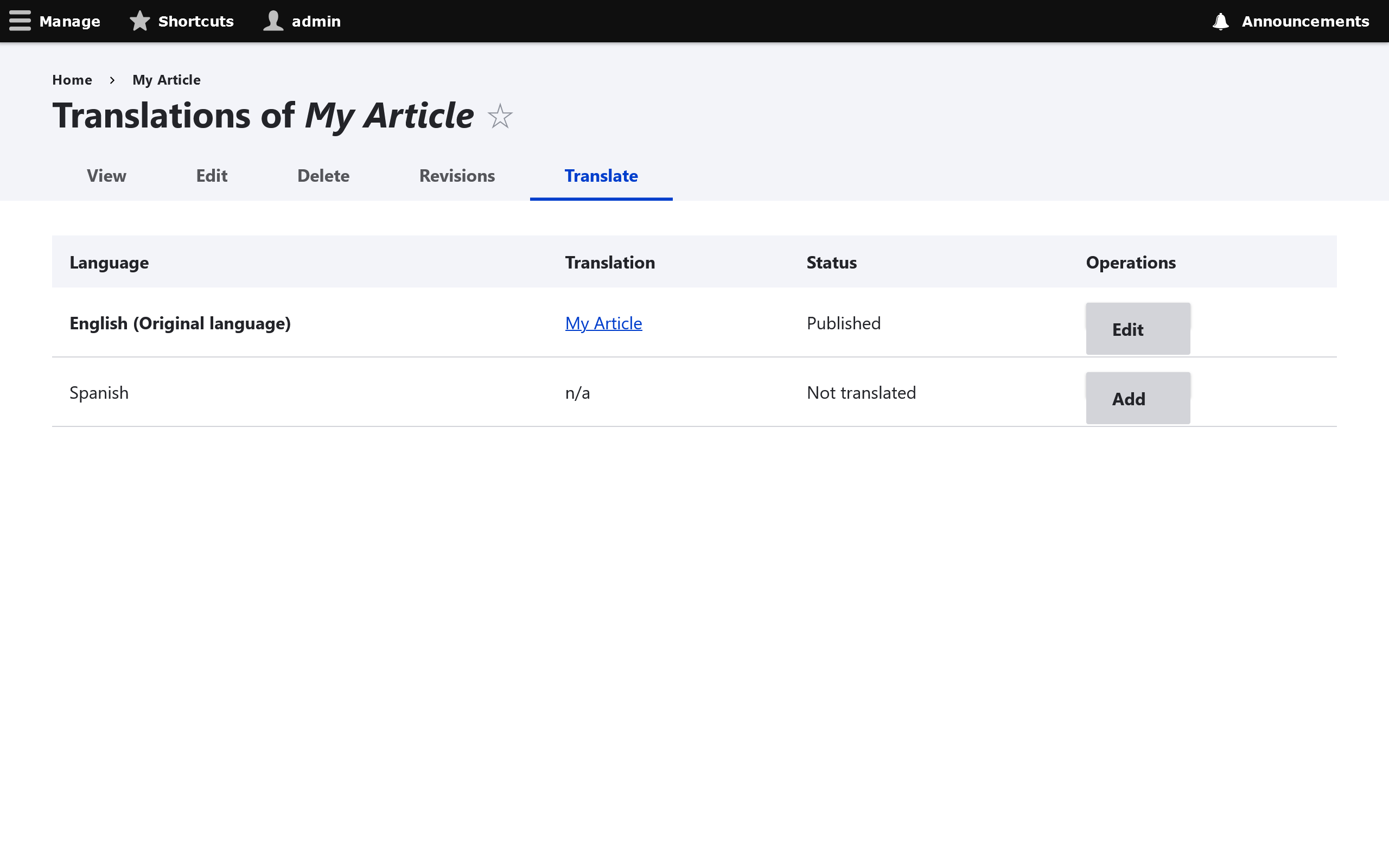
Specify the translated node content and then save. 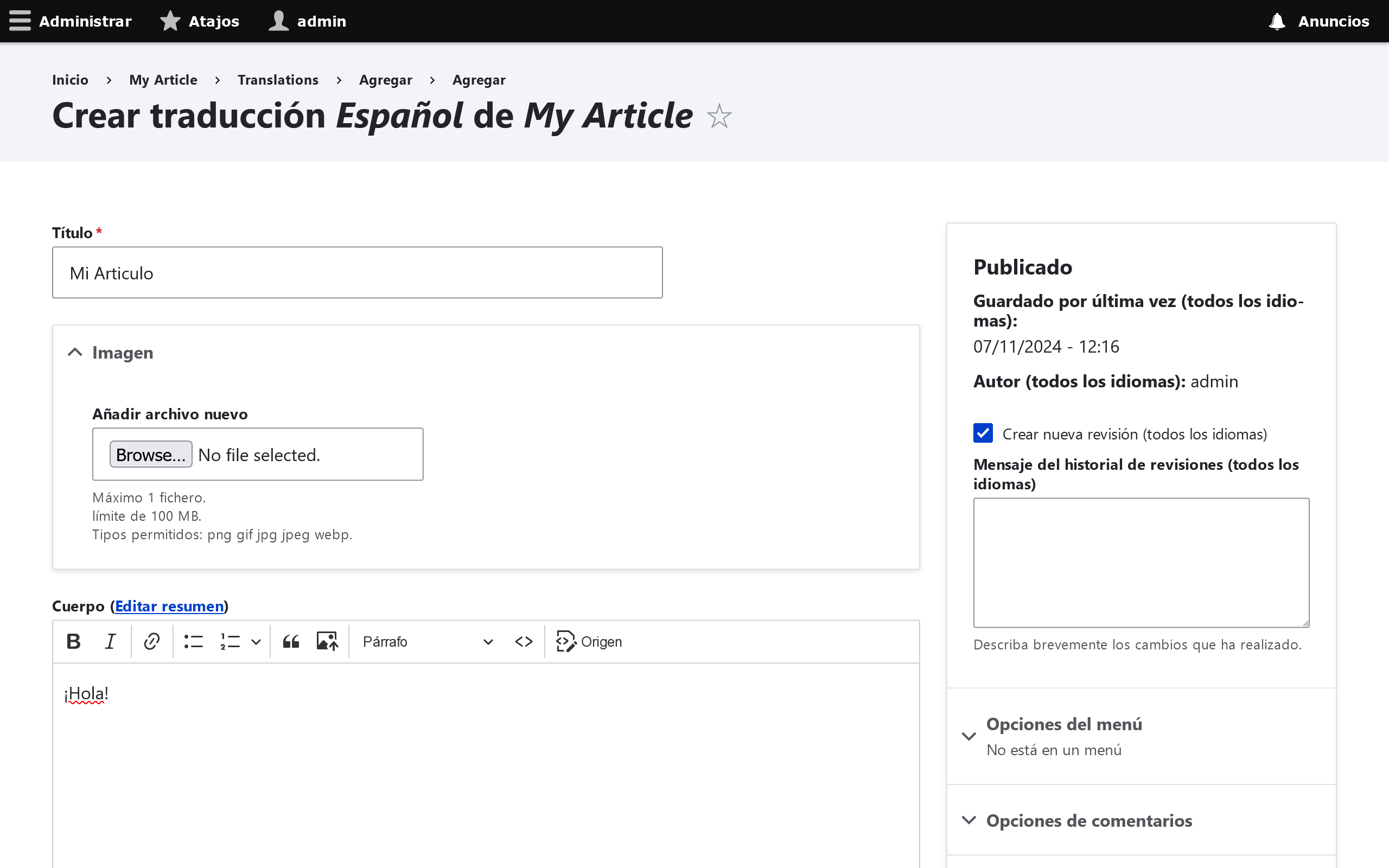
Configuration Translation Module
(machine name: config_translation)
From Choosing and installing multilingual modules:
Provides a translation interface for configuration. Allows you to translate text that is part of the configuration, such as field labels, the text used in Views, etc.
To translate configuration settings go to Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Configuration translation. 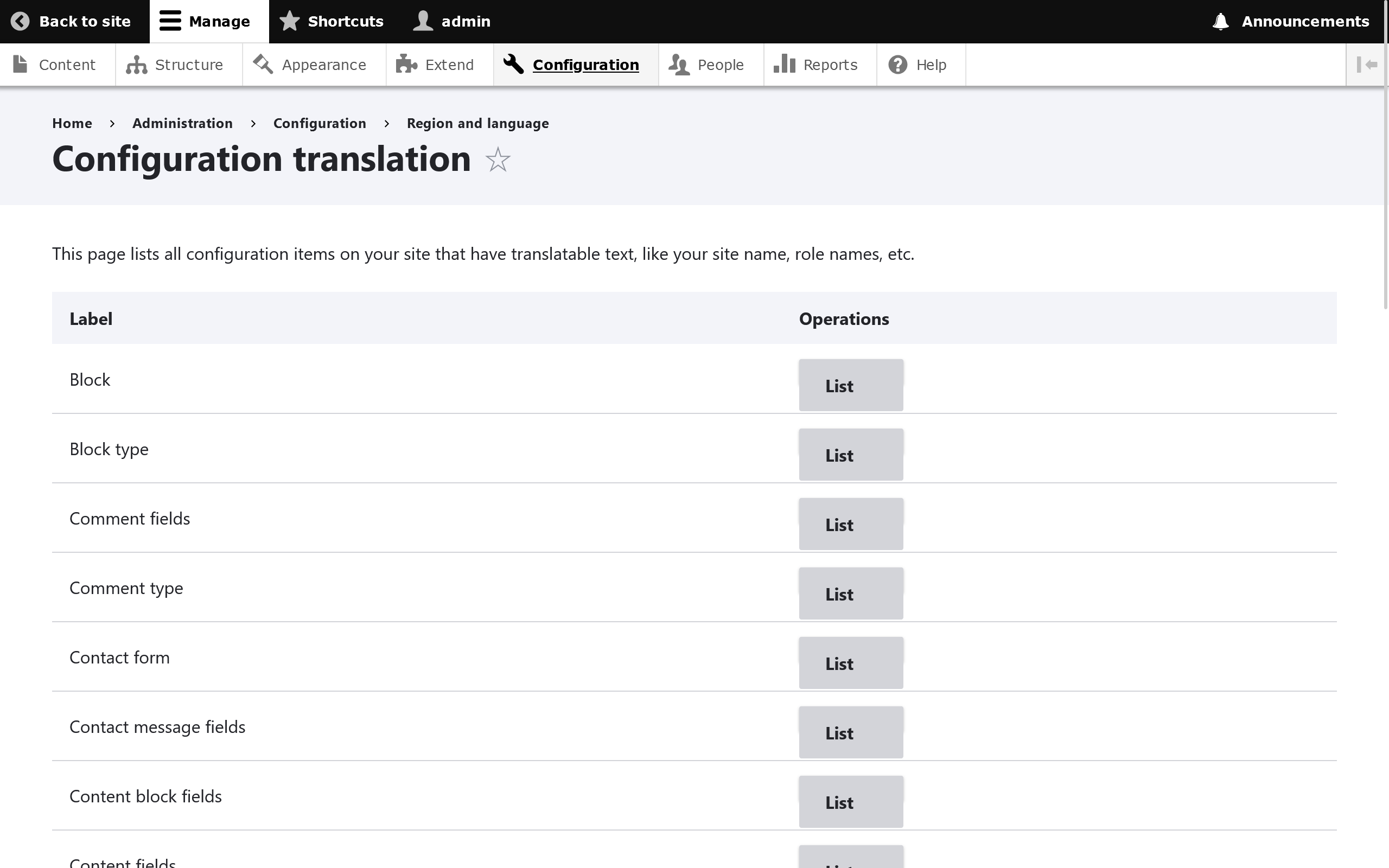
Find a configuration setting you wish to translate and click the Translate button. (Note: If you see a button that says List instead of Translate, this means you're in a parent group and must click through to get to more specific configuration settings.) 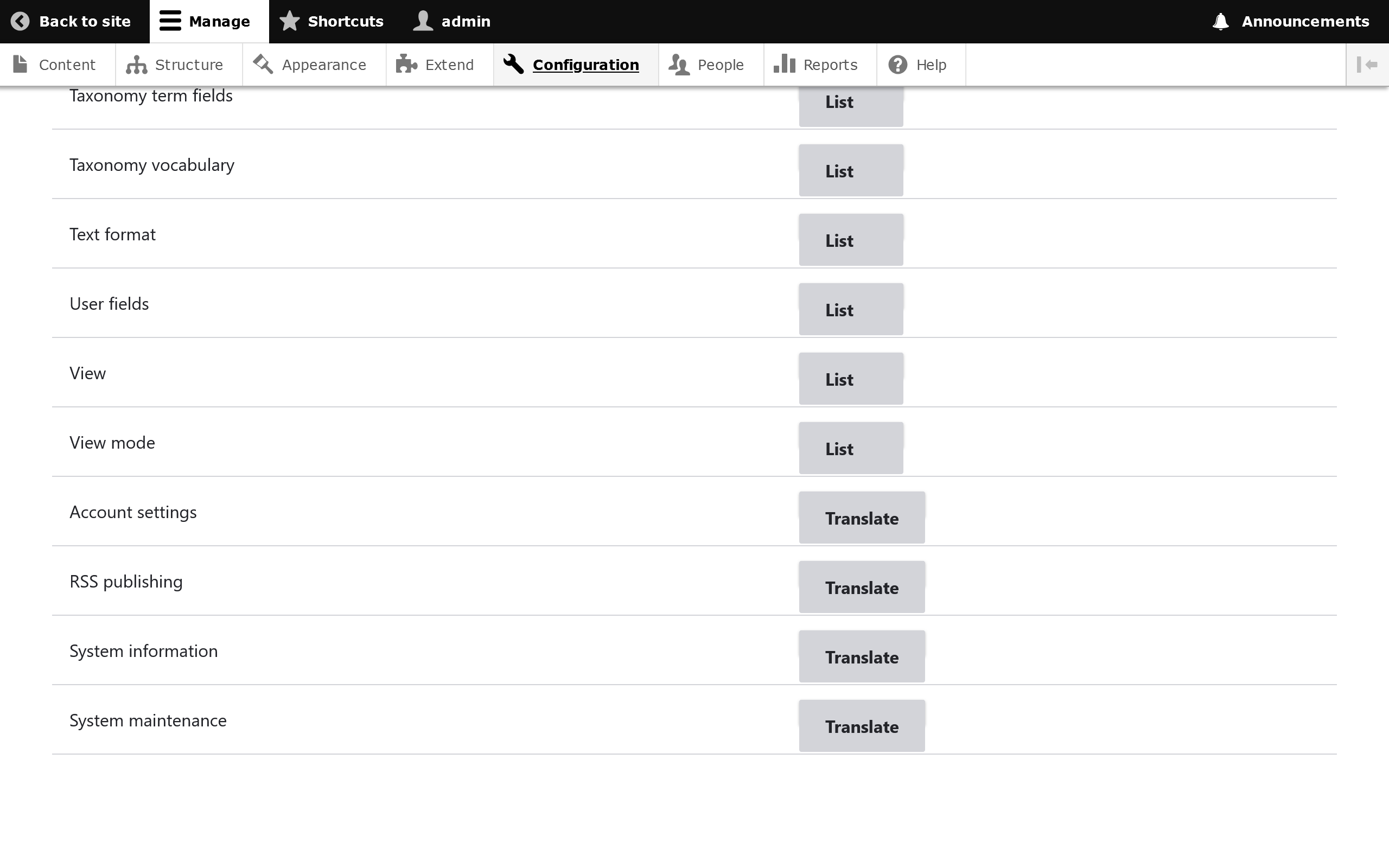
When you click Translate on a particular item, you should see the option to either add or edit an existing translation. 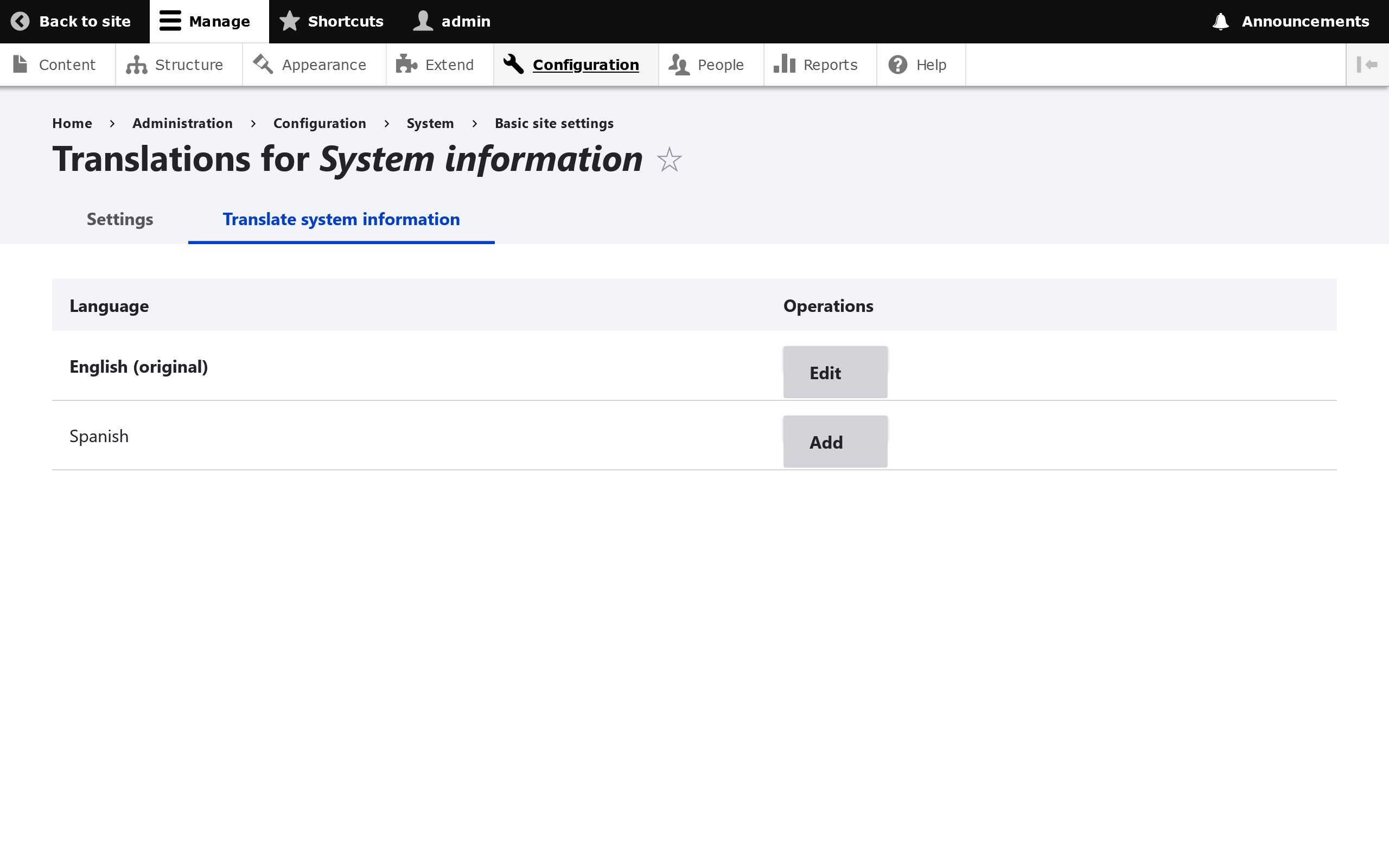
Edit the particular settings you wish to update and then click the Save Translation button. 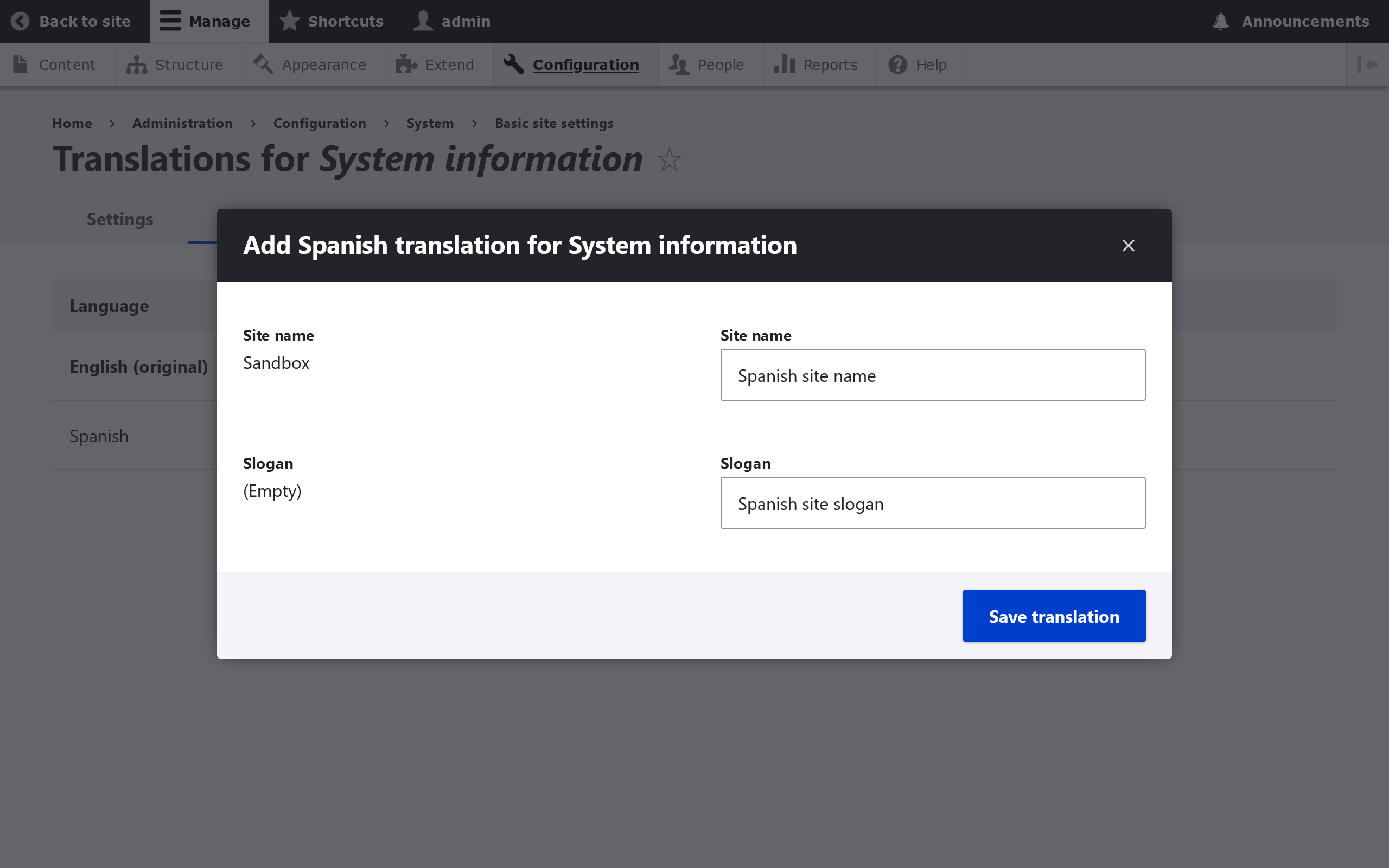
See Configuration Management for more information on managing configurations in Drupal.
Additional Resources
- drupal.org - Making Your Site Multilingual
- drupal.org - Multilingual Guide
- lingotek.com - Drupal 8 Multilingual APIs
- drupal.org - Enable Language Negotiation
Questions
How can we enable multilingual functionality on an existing Drupal site and What are four multilingual features in Drupal that provide multilingual functionality?
To enable Multilingual functionality on an existing site, go to "Extend" or /admin/modules and find the Multilingual section. Language is the base module required for multilingual, but you will likely want at least Content Translation as well, and the four core mulitlingual features are, Language Module, Interface Translation Module, Content Translation Module and Configuration Translation Module.
What is the purpose of the Language Module, How can we manage language support in Drupal?
The Language Module allows users to configure languages, determine how page languages are chosen, and apply languages to content. To manage language support go to Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Languages including adding or removing languages.
What is the purpose of the Content Translation Module, and configuration in Drupal?
Content Translation Module allows users to translate content entities, site content, including pages, taxonomy terms, blocks, etc., into different languages. To configure the translation module go to Configuration -> Regional and Language -> Configuration translation.
